This article is to simplify blockchain to business users.
Blockchain is an innovative way of combining the plus points of a few available technologies to meet some inherent business requirements. At its core, it uses a)distributed database and b) immutable database.
Distributed database means that the same database is shared with many users and each have a copy of the same in their systems. This is not a new concept and there are many different uses for this. Immutable database means that no data can be deleted or edited. Old data remains as is and new content gets just added to this database. Both these concepts, when put together, provides new value and opens up opportunities for having faith/trust in the data that is stored in such databases.
What is in it for businesses?
Businesses is a network of interested parties that exchange value. They trade in assets that are tangible (houses/ cars/ mobiles …) or intangibles (mortgages/ shares…). They maintain these asset ownership and value details in their own Accounting Ledger, which may be in the form of ERP software or physical ledgers. The network participants need not necessarily trust each other and hence have a host of intermediaries (banks/ brokers/ agents …) to glue the network. This comes at a cost and has its own inefficiencies, including reconciliation efforts.
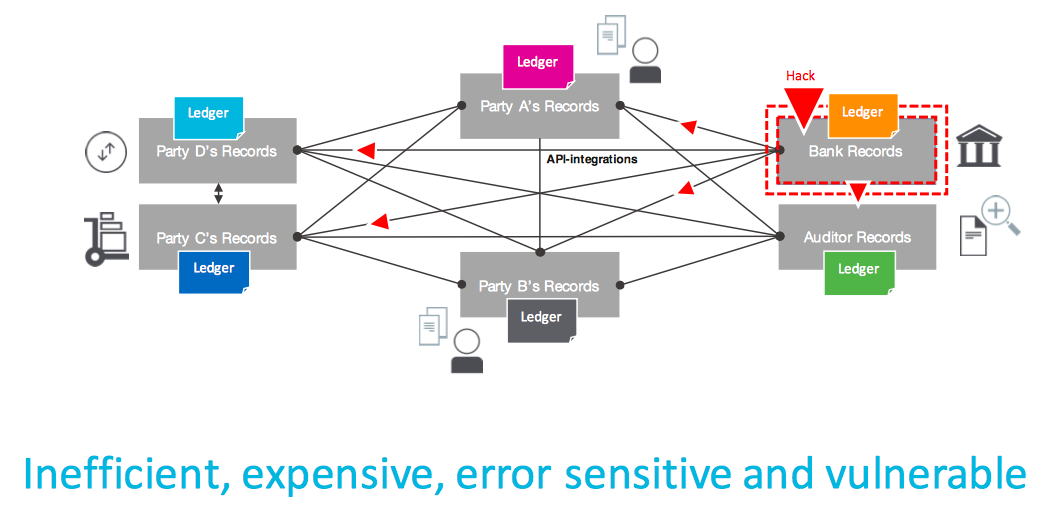
Source: IBM document
Now imagine a common Ledger or Accounting book in which each of these asset exchanges are maintained. Make that ledger immutable, thereby participants know that no entry gets lost or edited. Now, keep a copy of the ledger with each of the participants and thus there is no single owner of the ledger and all the participants of the network are the owners. This brings in the element of trust across the participants, without any intermediary. We will see in a separate blog on consensus / approval mechanism for the transactions to get into a shared ledger.
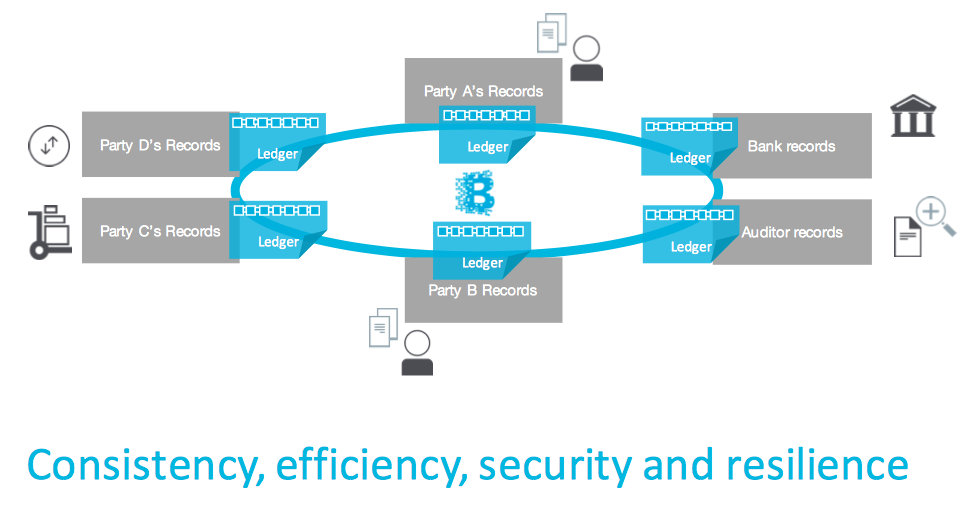
Source: IBM document
Blockchain for business is a distributed shared immutable ledger of assets exchanged across its network participants.
Why is it named blockchain?
The transaction contents (e.g. Time Period 1) are stored in a block and cryptographically sealed with a hash. The next set of transactions (e.g. Time Period 2) are put in the next block and this block includes a link to the previous block hash. Now this block 2 is cryptographically sealed again. Thus the database is a series of blocks which are linked to their previous blocks. Thus the name blockchain.
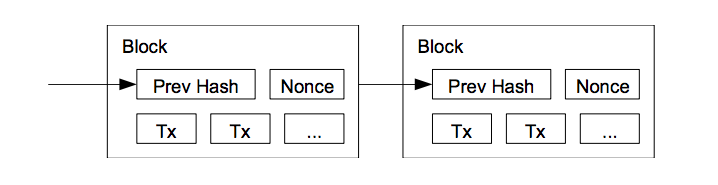 Source: Bitcoin paper
Source: Bitcoin paper
What is bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency which is run on a public permission less blockchain. Permission less means that any one can participate in this bitcoin network and exchange this bitcoin cryptocurrency. The asset being exchanged is cryptocurrency called bitcoin.
Permissioned blockchain for businesses:
For business requirements, we are most likely to have permissioned network, by which the participants of the network are controlled and only selected participants are included in the network.
Inherent advantages of a blockchain network:
Provenance:
Shared ledger is immutable and the blocks of transactions are linked to their previous ones, going back to the origin. Imagine a car with a Vin number in a blockchain network. Over its lifecycle , the ownership of this asset changes multiple times. Authorized participants will get to see the complete history of exchange of ownership of this asset across its life cycle. The transactions are immutable and are linked and hence the complete link is established. Thus, at any point of time, the network knows the exact provenance of an asset. Extend this logic to Land Records, Supply chain of perishables, foods, medicines , diamonds …
Immutability:
A blockchain is immutable and all the database contents remain for ever. No participant can change/ edit any content in their copy of the database. The underlying cryptography of hashing a block content and including this hash in the next block ensures that any change in a previous block would corrupt the chain. This corruption of data would be easily visible to the network. The network has the uncorrupted database with many participants and there are easy mechanisms to self correct.
Finality:
The immutability and sharing of the same ledger content across all its participants provides a finality to the transaction and thus the trust to all its participants. The need for any reconciliation across participants is completely eliminated. Many subsequent business processes can function with this finality well established.
Related articles
Blockchain basics - Cryptography LinkedIn / GitHub
Blockchain basics - Merkle tree LinkedIn / GitHub
Blockchain basics - Byzantine fault tolerance LinkedIn / GitHub